Implement Attack Surface Reduction rules
You can use Attack Surface Reduction rules to help prevent actions and apps, which are often used by exploit-seeking malware to infect your organization’s devices. Each rule is identified by a unique identity known as a GUID (globally unique identifier). Table 3-3 describes the available Attack Surface Reduction rules and their respective GUIDs.
TABLE 3-3 Attack Surface Reduction rules
| Rule and description | GUID |
| Block executable content from email client and webmail. | be9ba2d9-53ea-4cdc-84e5-9B1eeee46550 |
| Block all Office applications from creating child processes. | d4f940ab-401b-4efc-aadc-ad5f3c50688a |
| Block Office applications from creating executable content. | 3b576869-a4eC-4529-8536-b80a7769e899 |
| Block Office applications from injecting code into other processes. | 75668c1f-73b5-4Cf0-bb93-3ecf5cb7cc84 |
| Block JavaScript or VBScript from launching downloaded executable content. | d3e037e1-3eb8-44c8-a917-57927947596d |
| Block execution of potentially obfuscated scripts. | 5beb7efe-fd9A-4556-801d-275e5ffc04cc |
| Block Win32 API calls from Office macros. | 92e97fa1-2edf-4476-bdd6-9dd0B4dddc7b |
| Block executable files from running unless they meet a prevalence, age, or trusted list criterion. | 01443614-cd74-433a-b99e-2ecdc07bfc25 |
| Use advanced protection against ransomware. | c1db55ab-c21a-4637-bb3f-a12568109d35 |
| Block credential stealing from the Windows local security authority subsystem (lsass.exe). | 9e6c4e1f-7d60-472f-ba1a-a39ef669e4b2 |
| Block process creations originating from PSExec and WMI commands. | d1e49aac-8f56-4280-b9ba-993a6d77406c |
| Block untrusted and unsigned processes that run from USB. | b2b3f03d-6a65-4f7b-a9c7-1c7ef74a9ba4 |
| Block Office communication applications from creating child processes. | 26190899-1602-49e8-8b27-eb1d0a1ce869 |
| Block Adobe Reader from creating child processes. | 7674ba52-37eb-4a4f-a9a1-f0f9a1619a2c |
To enable specific Attack Surface Reduction rules, you can use GPOs or Windows PowerShell. To use GPOs to manage Attack Surface Reduction rules, use the following procedure:
- On a domain controller, open the appropriate GPO for editing.
- In the Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Microsoft Defender Antivirus > Microsoft Defender Exploit Guard > Attack Surface Reduction.
- Select Configure Attack Surface Reduction rules.
- Select Enabled, as displayed in Figure 3-5.
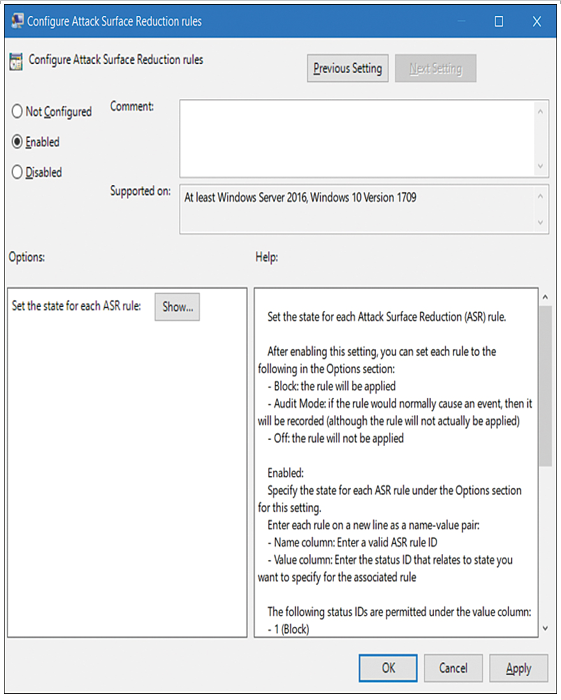
Figure 3-5 Configuring Attack Surface Reduction rules
5. Select Show. In the Value Name box in the Show Contents window, enter the relevant GUID, as displayed in Figure 3-6. (Review Table 3-3 for more details about GUIDs.)
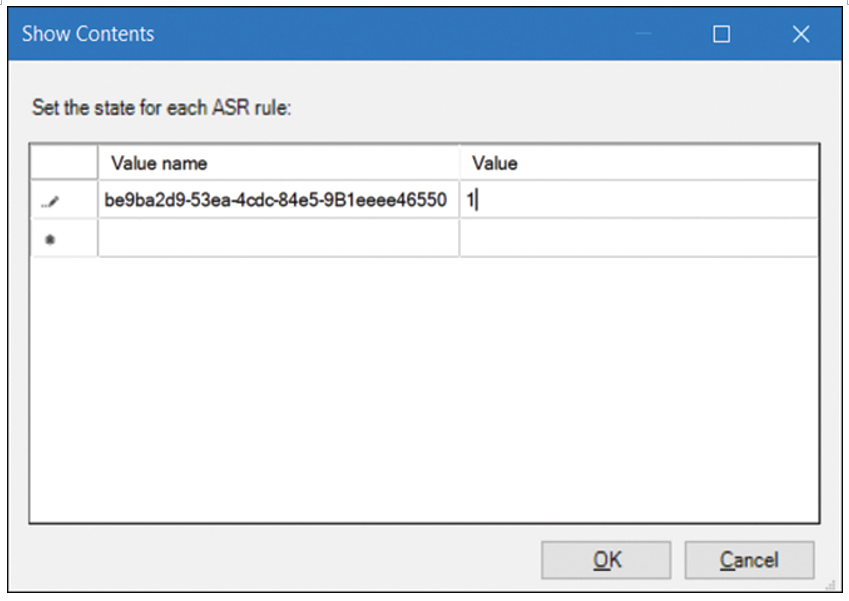
Figure 3-6 Specifying an ASR rule
6. In the Value box, enter one of the following:
- 0 to disable the specific rule
- 1 to enable block mode
- 2 to enable audit mode only
7. Select OK twice, and then close the Group Policy Management Editor.
To use Windows PowerShell (Administrator) to configure these rules, you can use the Set-MpPreference cmdlet, as displayed in the following code snippet:
Click here to view code image
Set-MpPreference -AttackSurfaceReductionRules_Ids <rule ID> –
AttackSurfaceReductionRules_Actions Enabled
Need More Review? Enable Attack Surface Reduction Rules
To review further details about configuring Attack Surface Reduction rules, refer to the Microsoft website at https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/microsoft-defender-atp/enable-attack-surface-reduction.



